Contract of Bailment: Legal Issues and Case Studies
Contract of Bailment in Law of Contract
Meaning and Definition of Bailment:
According to Section 148 of the Contract Act
"A bailment is the delivery of goods by one person to another for some purpose, upon a contract that they shall, when the purpose is accomplished, be returned or otherwise disposed of according to the directions of the person delivering them".
 |
| Bailment and its Kinds in Law of Contract |
Thus, a bailment is the legal relation that arises whenever one person delivers Possession of personal property to another person under an agreement by which the latter is under a duty to return the identical property to the former or to deliver or dispose of according to the agreement.
A bailment can also be defined as a voluntary transfer of the possession of goods by the owner to another person, who is not his servant, under a contract that such other person shall do something with the goods or hold them or return them to the owner, or deliver them according to his order.
If a person already in possession of the goods of another contracts to hold them as a bailee, he thereby becomes the bailee, and the owner becomes the bailor.
Concept of law of Bailment:
Deposit for safe custody in Bank's lockers, Scope: Deposit for safe custody was a branch of law of Bailment and Bailment was delivery of movable property by one person (the bailor to another, the bailee) on condition that it shall, in due course, be redelivered to bailor on his/her order Person who hired a locker retained some control over it by having one key with himself but if said locker could be operated without any key then at once any impediment in the way of control and possession of the Bank to whom the locker belonged and in those strong-room it was to be found, would be removed and it could be said that such Bank was in position of a bailee. When Bank was bailee, then care which Bank was obliged to take was such care as an ordinarily efficient and prudent person could take in similar circumstances. Bank would not be liable if property held in safe custody was destroyed by fire or otherwise, lost or stolen unless there was negligence on the part of Bank, and degree of negligence required to establish liability would depend on the relevant circumstances of a case. 2021 PLD 28 Karachi High Court
Parties in Contract of Bailment:
There are two parties to a contract of bailment:
Bailor: The person delivering the goods is called the bailor.
Bailee: The person to whom the goods are delivered is called the “bailee.
Illustration:
- a) A delivers a piece of cloth to B to make a suit. There is a contract of bailment between A and B.
- b) A lends a book to B for examination, there is contract of bailment between A and B.
- c) A delivers a watch to B for repair. There is a contract of bailment.
Essential Features of Bailment:
The following are the essential features of a bailment.
1) Delivery under a Contract:
A bailment is based on a contract between bailor and bailee. The delivery of goods should be made for some purpose under a contract that when the purpose is accomplished the goods shall be returned to the bailor. If the goods are delivered without any contract i.e. by mistake, there is no bailment. It should also possess all the essentials of a valid contract.
Illustration: The plaintiff's ornaments, have been stolen, were recovered by the police and, while in police custody were stolen again. The plaintiff's action against the state for the loss was dismissed. (Ram Gulam vs Government of UP)
2) Specific Purpose:
The bailment of goods is always made for some purpose and is subject to the condition that when the purpose is accomplished the goods will be returned to the bailor or disposed of according to the directions of the bailor. If the person to whom the goods are delivered is not bound to return them to the person delivering them or to deal with them, there is bailment.
Illustrations:
- A gives his watch to B for repair. There is a bailment.
- The plaintiff delivered to the Treasury officer at Meerut nine Government Promissory notes for cancellation and consolidation into a single note of Rs.48,000. The defendant's servant misappropriated the notes. The plaintiff sued the state to hold them responsible as bailee’s. But his action failed. (Secretary of State vs Sheo Singh Rai)
(3) Transfer of Possession:
The important feature of bailment is the ‘transfer of possession’ by one person to another. ‘Transfer of possession’ should be distinguished from mere ‘custody’. One who has custody without possession, like a servant, or a guest using his host’s goods is not a bailee. The goods must be handed over to the bailee for the purpose of bailment.
Bailment may arise even when owner of goods has not consented to their possession by bailee at all. 1992 CLC 2412 KARACHI-HIGH-COURT-SINDH
(4) Delivery of Moveable Goods:
Under bailment only the movable goods are delivered. The movable goods are delivered by one person to another person (not being his servant). If a person already in possession of the goods of another, agrees to hold them as a bailee, he in this way becomes bailee though there is no actual delivery by way of bailment. The bailment is not completed until according to the agreement of the parties, the property is delivered to the bailee and accepted by him.
Illustration:
A buys a T.V. from B. The T, V. is ready for immediate delivery. A asks B to keep it with him for one hour so that A may buy other things from the market. B is now holding the T.V as bailee.
(5) No Change of Ownership:
Under bailment, it is only the possession that passes from the owner to the other and not the ownership, Mere custody without possession is not bailment, e.g. (a servant holding his master’s goods). If there is a change of ownership the transaction may be a Sale or exchange but is not a bailment.
(6) Return of Same Goods:
The bailee is under a duty to return or dispose of the same goods that were bailed and in the manner directed by the bailer. If the bailee has an option of paying money or of returning different property, there is no bailment. The deposit of money with a banker is not a bailment because there is no obligation to return the specific money as was deposited. But notes or other things deposited in a locker provided by a bank, it is a bailment.
2022 CLD 320 LAHORE-HIGH-COURT-LAHORE VITAL CHEMICALS CORPORATION VS SILK BANK LIMITED
Sections 148 & 172 of Contract Act
"Bailment " and "pledge "Distinguished Slight difference between Bailment and pledge is that in the case of Bailment deposit of goods is for a certain purpose to be returned after the purpose is accomplished but in case of pledge, goods are deposited as security to be kept till payment of debt is effected or a promise for which the goods were pledged is performed---Pledge is kind of Bailment and security.
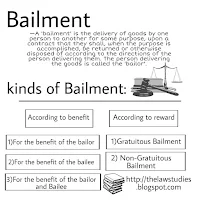
Kinds of Bailment:
Bailment may be classified as follows:
- (1) According to benefit
- (2) According to reward
(1) Benefit:
According to benefit, bailment can be grouped into three classes:
(a) For the benefit of the bailor:
Where the goods are delivered for safe custody to a neighbor, relative, or friend without any compensation to be paid.
(b) For the benefit of the bailee:
Where goods are delivered to the bailee to be used by him without any compensation to be charged from him. For example, A borrows B’s pen to use in the examination hall, the bailment is for the sole benefit of A, the bailee.
(c) For the benefit of the bailor and bailee:
Where the goods are delivered for the benefit of both the bailor and bailee.
For example, bailment for repair, hire, etc.
(2) Reward:
Bailments may also be classified into two classes according to reward.
(a) Gratuitous Bailment:
It is bailment in which neither the bailor nor the bailee is entitled to any remuneration. For example, lending a book to a friend, depositing goods for safe custody without any charges.
(b) Non-Gratuitous Bailment:
It is a bailment where the bailor or the bailee is entitled to a remuneration. For example Motor cars let out for hire, clothes given for Tailoring on charges.
Conclusion:
From the above discussion it has been cleared that bailment basically is a contract and legal relation that arises whenever one person hands over the possession of some property to another under an agreement with aim to return the same to him or dispose of according to his command.
Bailed goods suffering due to negligence of bailee's servant-Bailee liable even if servant dealt with goods for his own purpose and outside scope of authority-Shares in custody of stock-broker on behalf of client-Clandestine sale of such shares by servant for his own benefit-Stock-broker, held, liable and answerable for loss sustained by client 1965 PLD 259 KARACHI-HIGH-COURT-SINDH
Possible relevant/Expected Questions to the Topic that we have covered above:
Define bailment?
Explain the Essential Features of Bailment.
What are different kinds of Bailment?